4 Things to Consider in Choosing a College or Career School

Choose the college or career school for you with the U.S. Department of Education’s (ED) College Scorecard. Answer your questions about costs, graduation, debt, and typical earnings after enrollment so you can find the school that’s right for your future and your pocketbook.
A college or career school education could mean more money, more job options, and more freedom. Yet, with more than 5,600 college and career schools nationwide participating in federal student aid, deciding which school is right for you can be difficult. Maybe you want to attend a school with the best nursing program, the most study abroad options, or the best college basketball team—every person values different things.
However, it’s also important to remember that going to a college or career school is one of the biggest financial investments you will make. Just as important as academics and extracurricular activities are the financial factors: how much a school costs, whether students are likely to graduate on time, and if alumni are able to find good jobs and pay off their loans.
That is why the U.S. Department of Education developed College Scorecard. It provides clear information to answer all your questions about costs, graduation, debt, and typical earnings after enrollment.
As you’re considering schools, use College Scorecard to compare these four things.
1
Net Cost
For starters, you should consider how much you’ll actually be paying on a yearly basis. That’s not necessarily the sticker price—it’s the sticker price minus all the scholarships and grants that you may receive when enrolling in a college or career school. This is called average annual cost, and it’s important because it’s the average amount students actually pay out of pocket.
College Scorecard can show you the average annual cost of each school compared to the national midpoint. It can also give you a net price estimate for each school broken down by family income. Here’s an example:

2
Graduation Rate
Next, you should consider a school’s graduation rate as a factor. You can use College Scorecard to learn about the different ways degree-granting and nondegree-granting schools determine graduation rates.
You may want to attend a school that has a high graduation rate. A school’s graduation rate gives a good indication of whether students who attend that institution are likely to end up with a certificate or degree. For schools like community colleges, you may also want to look at the transfer rate if you’re planning on transferring to a four-year school after attending a two-year school.
Retention rate is the percentage of a school’s first-time, first-year undergraduate students who continue at that school the next year. For example, a student who studies full-time in the fall semester and keeps on studying in the program in the next fall semester is counted in this rate.
College Scorecard shows you each school’s graduation and retention rate:

3
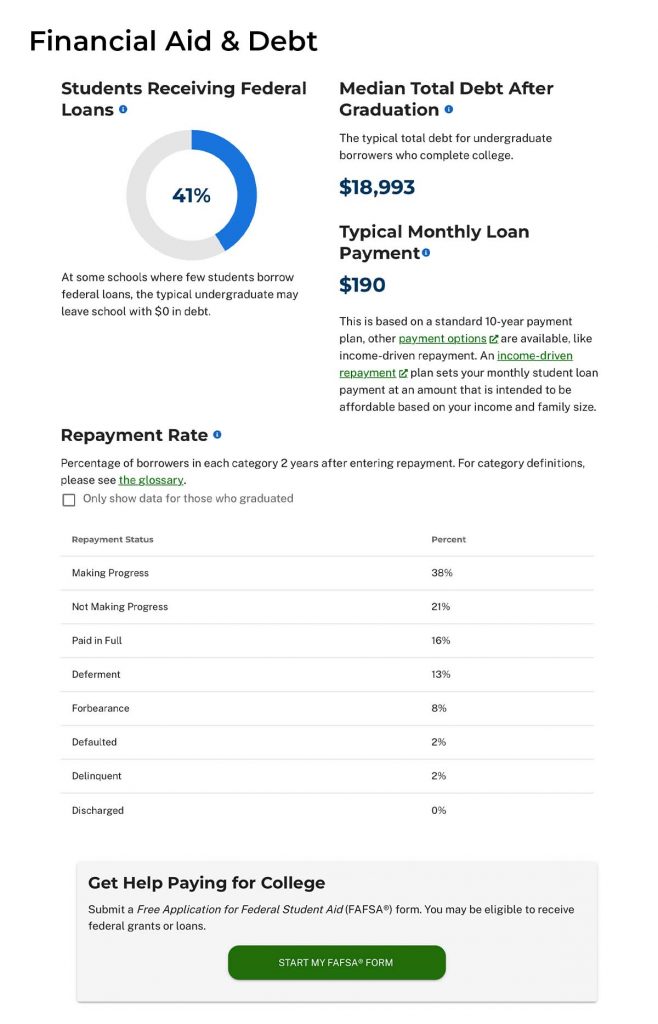
Students Paying Down Their Debt
In addition to costs, you may consider if students are able to repay their loans after attending a specific college or career school. College Scorecard can help you find out
- the proportion of students who borrow,
- the amount of debt that borrowers typically take on at a college or career school, and
- the percentage of borrowers who are able to repay that debt upon leaving.
This is one of the most important factors to consider, as you may not want to attend a college or career school where you’re expected to get lots of loans and have little chance of repaying them in the future.
4
Post-Enrollment Earnings
With the cost of higher education continuing to increase, salary has become a critical factor students and families take into account. Knowing how much students typically earn after attending a specific college or career school will help you find out if those students were able to land good paying jobs, pay off their student loans, and become financially secure.
Luckily, College Scorecard contains comprehensive and reliable data on post-enrollment earnings for students who attended all types of colleges and career schools. College Scorecard includes
- the proportion of former students earning over $31,000, which is the average earnings of high school graduates; and
- the median earnings of students 10 years after they enroll in a particular school.
Here’s an example of what College Scorecard will show you:

Selecting a college or career school is one of the most important decisions you will ever make. Are you ready to begin your search? If so, visit College Scorecard today!


